|
Jive reference manual
|
|
Jive reference manual
|
Constructs shape objects that encapsulate the geometrical properties of linear quadrilateral elements. More...
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static jem::Ref< InternalShape > | getShape (int ipCount=4, int bndIpCount=2) |
| Returns a shape with a specified number of integration points. More... | |
| static jem::Ref< InternalShape > | getShape (const Matrix &intPoints, const Vector &intWeights, const Matrix &bndIntPoints, const Vector &bndIntWeights) |
| Returns a shape with a specific set of integration points. More... | |
| static jem::Ref< InternalShape > | getShape (const Matrix &intPoints, const Vector &intWeights, const ShapeBoundary &boundary) |
| Returns a shape with a specific set of boundaries. More... | |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Public Types inherited from jive::geom::TypeDefs Public Types inherited from jive::geom::TypeDefs | |
| typedef jem::util::Properties | Properties |
| A type representing a set of properties. More... | |
| typedef util::Vector | Vector |
| A vector type. More... | |
| typedef util::Matrix | Matrix |
| A matrix type. More... | |
#include <jive/geom/Quad.h>
The LinearQuad class provides functions for constructing InternalShape objects that encapsulate the geometrical properties of quadrilateral elements with four nodes and bi-linear, isoparametric shape functions. The following figure shows how the nodes are numbered (left image) and where they are located in the local coordinate system (right image).
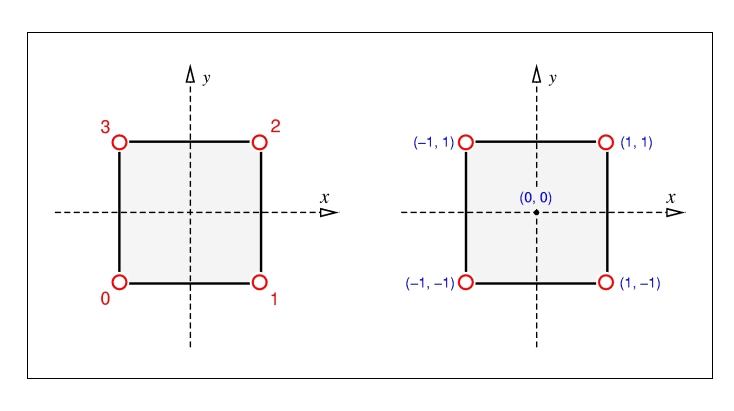
Note that the local node coordinates of a linear quadrilateral are identical to the node coordinates of a standard linear square.
A linear quadrilateral has four boundaries. The table below indicates which boundaries are attached to which nodes.
| Boundary index | Node indices |
| 0 | 0, 1 |
| 1 | 1, 2 |
| 2 | 2, 3 |
| 3 | 3, 0 |
The normals on the boundaries point away from the interior of the quadrilateral. The boundaries are normally represented by BoundaryShape objects that are constructed by the LinearBoundaryLine class. However, you can also specify your own set of BoundaryShape objects to be used.
Note that the LinearQuad class has only static members; it should be used as a mini name space.
QuadraticQuad, BiQuadraticQuad
|
static |
Returns an InternalShape object that encapsulates the geometrical properties of a linear quadrilateral element. The parameter ipCount specifies the number of integration points within the element. The parameter bndIpCount specifies the number of integration points on each boundary.
This function simply executes:
Note that the actual number of integration points within the element and on the boundaries may be different from ipCount and bndIpCount; read the documentation of the StdSquare and StdLine classes for more information.
| ipCount | - the number of integration points within the element. |
| bndIpCount | - the number of integration points on each boundary. |
InternalShape object representing a linear quadrilateral element.
|
static |
Returns an InternalShape object that represents a linear quadrilateral element with a specific set of integration points. The matrix intPoints should contain the local coordinates of the integration points within the element: intPoints(i,j) should be equal to the i-th local coordinate of the j-th integration point. The vector intWeights should contain the integration weights in the local coordinate system: intWeights[j] should be equal to the local integration weight associated with the j-th integration point.
The matrix bndIntPoints should contain the local coordinates of the integration points on each boundary. The vector bndIntWeights should contain the corresponding integration weights, also in the local coordinate system of the boundaries (see the documentation of the LinearBoundaryLine class for more information).
Note that all the input arrays are copied by reference. You should not modify the contents of these arrays after calling this function.
You can use the StdSquare and StdLine classes to compute the integration point coordinates and weights. Here is an example:
| intPoints | - a matrix containing the local coordinates of the integration points within the element. |
| intWeights | - a vector containing the weights of the internal integration points in the local coordinate system. |
| bndIntPoints | - a matrix containing the local coordinates of the integration points on each boundary. |
| bndIntWeights | - a vector containing the weights of the boundary integration points in the local coordinate system of the boundaries. |
intPoints.size(0) == 2 &&
intPoints.size(1) == intWeights.size() &&
bndIntPoints.size(0) == 1 &&
bndIntPoints.size(1) == bndIntWeights.size() InternalShape object that encapsulates the geometrical properties of a linear quadrilateral element.
|
static |
Returns an InternalShape object that represents a linear quadrilateral element with a specific set of integration points and boundaries. The matrix intPoints should contain the local coordinates of the integration points within the element: intPoints(i,j) should be equal to the i-th local coordinate of the j-th integration point. The vector intWeights should contain the integration weights in the local coordinate system: intWeights[j] should be equal to the local integration weight associated with the j-th integration point.
The ShapeBoundary object boundary specifies the boundaries to be associated with the returned shape object.
Note that all the two input arrays and the members of the ShapeBoundary object are copied by reference. You should not modify the contents of these arrays and members after calling this function.
| intPoints | - a matrix containing the local coordinates of the integration points within the element. |
| intWeights | - a vector containing the weights of the internal integration points in the local coordinate system. |
| boundary | - the boundaries of the shape object that is returned by this function. |
intPoints.size(0) == 2 &&
intPoints.size(1) == intWeights.size() InternalShape object that encapsulates the geometrical properties of a linear quadrilateral element.